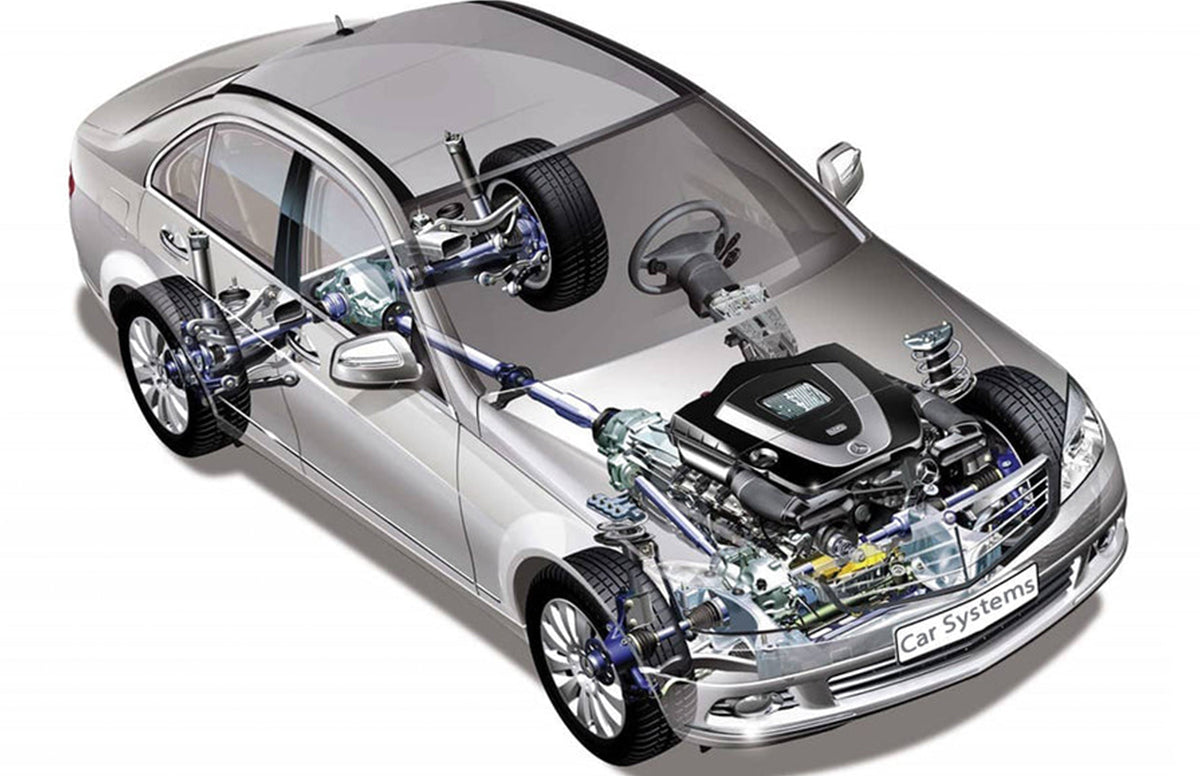
The world's first car was successfully developed by German Karl Benz in October 1885! Today, automobiles come in many forms according to different uses. Many automakers have added their own flair to these forms. Even car owners have done a lot of work to make more changes. The required functions of a car determine the unique design of the car as a whole and each part of its construction. Let's briefly introduce the main structure of the car!
A car is composed of many complex parts, and the external shape and internal structure of different cars may be different, but from the perspective of the overall structure, a car is generally composed of four basic parts such as engine, chassis, body, and electrical equipment.

1. Engine System
The car engine system is where fuel and air are input and converted into output power.
The process involves the mixing of fuel and air and the compression of the mixture. The spark plug then ignites this pressurized mixture, creating an explosion or "burn" that provides the power the car needs to move forward.
Internal Combustion Engine
Internal combustion engines can be of one of two types - gasoline or diesel. Most cars run on gasoline, and heavy-duty vehicles usually run on diesel fuel.
Fuel Injection
Whether it's the gasoline or diesel fueling your vehicle, it needs to be supplied to the engine at the right time and amount.
2. Power Transmission System
The main role of the engine system is to generate power, which needs to pass through many parts of the car and to the wheels and then onto the road to move the vehicle.
Usually, transfer systems come in automatic or manual form. With a manual transmission, you can shift gears yourself as needed, while an automatic transmission does it for you. With the development of modern driving techniques, other types of automatic and manual transmissions have also been developed, such as power shift transmissions and CVT transmissions.
Clutch
Cars with manual transmissions have a component called a clutch. The clutch works between the shaft from the engine and the shaft connected to the wheels.
The clutch engages and disengages the power transmission between the two shafts. So even though the engine's shaft is spinning all the time, it won't necessarily turn the car's wheels unless the clutch allows it.
CVT
In some cases, automakers prefer to use a CVT or continuously variable transmission.
You'll see that a traditional transmission moves from one gear to the next (eg, first, second, etc.), with each gear representing a specific gear ratio. The CVT doesn't move from one gear to another in this way. Instead, it gradually moves between different gear ratios.
3. Brake System
How do the brakes work? They create friction that hinders the car's movement, gradually reducing speed when the driver depresses the brake pedal.
This process can cause a lot of wear on some brake components, which is why regular maintenance of the brake system is critical. In a car, one of the most replaced parts is the brake pad, which is where friction occurs.
Anti-lock Brakes and Power Brakes
Many modern cars come with ABS or anti-lock braking systems and power brakes as standard features.
ABS ensures that your car's tires don't lock up completely when braking hard, preventing the vehicle from slipping and losing control. Dynamic brakes, on the other hand, amplify the force applied to the brake pedal.
4. Steering, Suspension and Tires
The most commonly used parts in a car are the steering, suspension and tires of the car.
How Steering Works
Steering is critical to controlling the direction in which the car is moving. Manual steering can be very tiring for the driver, especially on longer drives and heavier vehicles.
Thankfully, we now have power steering systems that increase the amount of steering effort the driver puts on the steering wheel, reducing the arm force required for steering.
Suspension System
If the ride is very bumpy, any shock and vibration from the wheels will be felt throughout the vehicle, making the entire trip very uncomfortable and more likely a safety hazard! For this reason, modern cars have suspension systems.
The suspension system includes shock absorbers, springs, and rods that connect the wheels to the vehicle.
Generally speaking, suspension systems fall into three categories: independent, dependent and semi-independent.
Tire
Tires actually work by spinning and gripping the road, creating the friction that moves the car forward.
They work best when the tires are filled with the right amount of air.
Today, tire pressure sensors are also a common feature. Some are standard features on new cars, but there are plenty of aftermarket options too.
The car engine system is where fuel and air are input and converted into output power.
The process involves the mixing of fuel and air and the compression of the mixture. The spark plug then ignites this pressurized mixture, creating an explosion or "burn" that provides the power the car needs to move forward.
Internal Combustion Engine
Internal combustion engines can be of one of two types - gasoline or diesel. Most cars run on gasoline, and heavy-duty vehicles usually run on diesel fuel.
Fuel Injection
Whether it's the gasoline or diesel fueling your vehicle, it needs to be supplied to the engine at the right time and amount.
2. Power Transmission System
The main role of the engine system is to generate power, which needs to pass through many parts of the car and to the wheels and then onto the road to move the vehicle.
Usually, transfer systems come in automatic or manual form. With a manual transmission, you can shift gears yourself as needed, while an automatic transmission does it for you. With the development of modern driving techniques, other types of automatic and manual transmissions have also been developed, such as power shift transmissions and CVT transmissions.
Clutch
Cars with manual transmissions have a component called a clutch. The clutch works between the shaft from the engine and the shaft connected to the wheels.
The clutch engages and disengages the power transmission between the two shafts. So even though the engine's shaft is spinning all the time, it won't necessarily turn the car's wheels unless the clutch allows it.
CVT
In some cases, automakers prefer to use a CVT or continuously variable transmission.
You'll see that a traditional transmission moves from one gear to the next (eg, first, second, etc.), with each gear representing a specific gear ratio. The CVT doesn't move from one gear to another in this way. Instead, it gradually moves between different gear ratios.
3. Brake System
How do the brakes work? They create friction that hinders the car's movement, gradually reducing speed when the driver depresses the brake pedal.
This process can cause a lot of wear on some brake components, which is why regular maintenance of the brake system is critical. In a car, one of the most replaced parts is the brake pad, which is where friction occurs.
Anti-lock Brakes and Power Brakes
Many modern cars come with ABS or anti-lock braking systems and power brakes as standard features.
ABS ensures that your car's tires don't lock up completely when braking hard, preventing the vehicle from slipping and losing control. Dynamic brakes, on the other hand, amplify the force applied to the brake pedal.
4. Steering, Suspension and Tires
The most commonly used parts in a car are the steering, suspension and tires of the car.
How Steering Works
Steering is critical to controlling the direction in which the car is moving. Manual steering can be very tiring for the driver, especially on longer drives and heavier vehicles.
Thankfully, we now have power steering systems that increase the amount of steering effort the driver puts on the steering wheel, reducing the arm force required for steering.
Suspension System
If the ride is very bumpy, any shock and vibration from the wheels will be felt throughout the vehicle, making the entire trip very uncomfortable and more likely a safety hazard! For this reason, modern cars have suspension systems.
The suspension system includes shock absorbers, springs, and rods that connect the wheels to the vehicle.
Generally speaking, suspension systems fall into three categories: independent, dependent and semi-independent.
Tire
Tires actually work by spinning and gripping the road, creating the friction that moves the car forward.
They work best when the tires are filled with the right amount of air.
Today, tire pressure sensors are also a common feature. Some are standard features on new cars, but there are plenty of aftermarket options too.
5. Electrical System
Cars don't just rely on mechanical auto parts; they also rely on electrical systems. The two systems are highly interdependent, and in modern cars it is almost impossible for one to operate without the other.
Battery
The heart of the electrical system is the battery. This is where electricity is stored before being distributed to the rest of the car. Without a working battery, the ignition system won't work and the car won't start at all.
Ignition System
When you turn the key in the ignition, the system draws power from the battery and uses it to create sparks in the engine's spark plugs. This is the first step in the combustion process, where the engine burns fuel and air to generate electricity. The ignition failed and the car wouldn't start at all.
Fuses and Connectors
Just like any electrical system, the electrical system in a car relies on fuses and connectors. Fuses provide protection by ensuring that electrical surges do not damage any electrical components. Connectors and wiring, on the other hand, conduct power directly from the battery to car components such as lights and even the on-board computer.
Car Computer(ECU)
The use of in-vehicle computers has increased in recent years. In this context, we do not mean any computer system that provides information or entertainment to the driver or passengers. Instead, we're referring to the computer that regulates the car's performance.
Examples of these computer systems are a powertrain control module (PCM), an engine control module (ECM), a transmission control module (TCM), and an automobile's immobilizer. The Power Control Module (PCM) is the brain of the car, coordinating the functions of the various components and systems of the car. If the vehicle is stolen, the immobilizer can be activated remotely to shut down the entire vehicle.
6. Exhaust System
In addition to power, an internal combustion engine produces two things: exhaust gas and noise.
These gases are toxic to humans and harmful to the environment. At the same time, loud noise is a serious nuisance for everyone in the vicinity of the vehicle, which is why the government has laws in place to regulate these two by-products from cars.
Cars manage these by-products through the exhaust system, which reduces exhaust gas and noise and safely exits the engine cylinders and vehicle. As part of this process, it also reduces harmful emissions and noise through catalytic converters and mufflers.
Catalytic Converter
In car exhaust systems, catalytic converters absorb toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, nitrous oxide, and hydrocarbons and convert them into harmless water and carbon dioxide.
Silencer
The muffler works by letting the exhaust sound bounce inside it. As the sound waves bounce off the surface, they gradually weaken to acceptable levels. When those sound waves come out of the exhaust, they will just be soft sounds.
7. Car Cooling System
The internal combustion engine and other parts of the car tend to get very hot under the hood. This is normal as long as it doesn't overheat. Cars have a car cooling system to keep them from overheating.
It consists of a water pump, thermostat, radiator, fan and other smaller components. This system circulates coolant through the interior of the engine to absorb heat. The coolant then passes through the radiator and the heat is released to the environment.
Knowing these systems will also help you understand the car better, at least, having this knowledge will make it easier for you to understand when which parts of the car need servicing or repairing!
Cars don't just rely on mechanical auto parts; they also rely on electrical systems. The two systems are highly interdependent, and in modern cars it is almost impossible for one to operate without the other.
Battery
The heart of the electrical system is the battery. This is where electricity is stored before being distributed to the rest of the car. Without a working battery, the ignition system won't work and the car won't start at all.
Ignition System
When you turn the key in the ignition, the system draws power from the battery and uses it to create sparks in the engine's spark plugs. This is the first step in the combustion process, where the engine burns fuel and air to generate electricity. The ignition failed and the car wouldn't start at all.
Fuses and Connectors
Just like any electrical system, the electrical system in a car relies on fuses and connectors. Fuses provide protection by ensuring that electrical surges do not damage any electrical components. Connectors and wiring, on the other hand, conduct power directly from the battery to car components such as lights and even the on-board computer.
Car Computer(ECU)
The use of in-vehicle computers has increased in recent years. In this context, we do not mean any computer system that provides information or entertainment to the driver or passengers. Instead, we're referring to the computer that regulates the car's performance.
Examples of these computer systems are a powertrain control module (PCM), an engine control module (ECM), a transmission control module (TCM), and an automobile's immobilizer. The Power Control Module (PCM) is the brain of the car, coordinating the functions of the various components and systems of the car. If the vehicle is stolen, the immobilizer can be activated remotely to shut down the entire vehicle.
6. Exhaust System
In addition to power, an internal combustion engine produces two things: exhaust gas and noise.
These gases are toxic to humans and harmful to the environment. At the same time, loud noise is a serious nuisance for everyone in the vicinity of the vehicle, which is why the government has laws in place to regulate these two by-products from cars.
Cars manage these by-products through the exhaust system, which reduces exhaust gas and noise and safely exits the engine cylinders and vehicle. As part of this process, it also reduces harmful emissions and noise through catalytic converters and mufflers.
Catalytic Converter
In car exhaust systems, catalytic converters absorb toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, nitrous oxide, and hydrocarbons and convert them into harmless water and carbon dioxide.
Silencer
The muffler works by letting the exhaust sound bounce inside it. As the sound waves bounce off the surface, they gradually weaken to acceptable levels. When those sound waves come out of the exhaust, they will just be soft sounds.
7. Car Cooling System
The internal combustion engine and other parts of the car tend to get very hot under the hood. This is normal as long as it doesn't overheat. Cars have a car cooling system to keep them from overheating.
It consists of a water pump, thermostat, radiator, fan and other smaller components. This system circulates coolant through the interior of the engine to absorb heat. The coolant then passes through the radiator and the heat is released to the environment.
Knowing these systems will also help you understand the car better, at least, having this knowledge will make it easier for you to understand when which parts of the car need servicing or repairing!